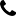A Sustainable Alternative: The Growing Popularity of Spun Silk Fabric
Content
Understanding Spun Silk Fabric as a Sustainable Textile Option
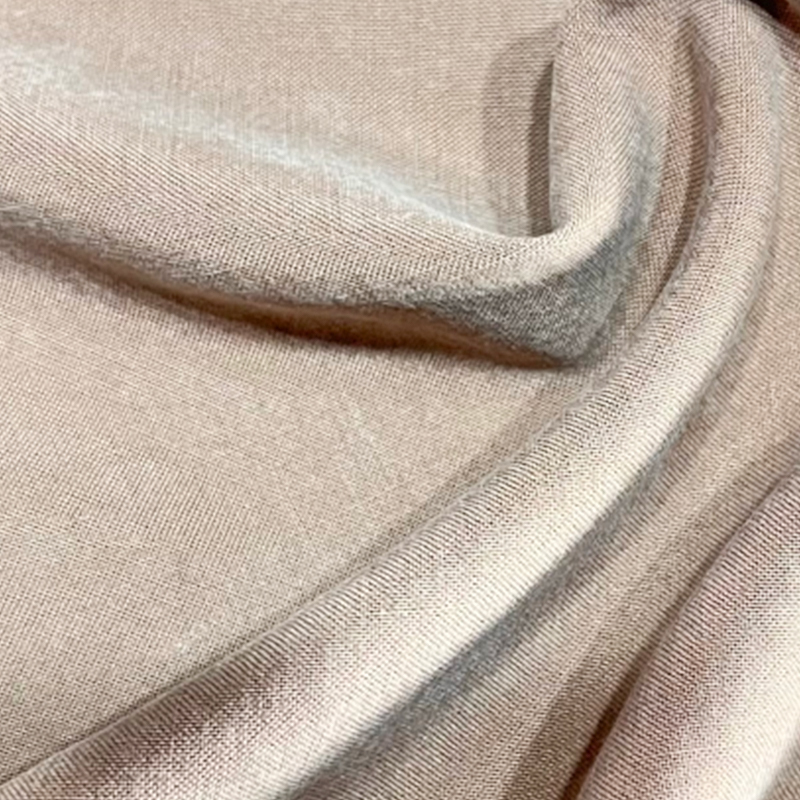
Spun silk fabric is increasingly recognized as a sustainable alternative within the silk textile category. Unlike traditional filament silk, spun silk is produced from shorter silk fibers that remain after the reeling process. These fibers are spun into yarn using methods similar to cotton spinning, allowing silk resources to be utilized more efficiently. This approach reduces material waste while retaining the natural qualities associated with silk, such as breathability, softness, and temperature adaptability.
From a sustainability perspective, spun silk aligns with responsible material use by maximizing fiber yield from each cocoon. Rather than discarding irregular or broken fibers, manufacturers convert them into usable yarn, supporting a more resource-conscious production model that appeals to brands focused on environmental responsibility.

How Spun Silk Reduces Material Waste in Silk Production
In conventional silk manufacturing, long continuous filaments are prioritized for luxury fabrics, while shorter fibers were historically underutilized. Spun silk production directly addresses this inefficiency by incorporating these leftover fibers into the supply chain. This practice lowers raw material loss and increases the overall output per batch of cocoons.
- Utilizes short silk fibers that cannot be reeled into filament silk
- Decreases reliance on additional raw silk harvesting
- Supports more complete use of existing silk resources
By extending the usability of silk fibers, spun silk contributes to a more circular production mindset, which is increasingly valued in sustainable textile sourcing.
Environmental Advantages Compared to Filament Silk
Spun silk offers several environmental advantages when compared with filament silk, particularly in energy and processing requirements. The spinning process is less dependent on maintaining long, unbroken fibers, which reduces strict quality control measures and associated energy use.
| Aspect | Spun Silk Fabric | Filament Silk Fabric |
| Fiber Utilization | High use of short fibers | Limited to long filaments |
| Production Waste | Lower overall waste | Higher leftover fiber waste |
| Energy Sensitivity | More flexible processing | Requires strict control |
Practical Applications Driving Market Demand
The growing popularity of spun silk fabric is closely linked to its practical performance across apparel and home textile applications. Its matte finish, soft hand feel, and balanced drape make it suitable for products that prioritize comfort and daily wear rather than decorative sheen.
Apparel and Fashion Use
In clothing production, spun silk is commonly selected for blouses, dresses, linings, and scarves. The fabric offers improved breathability and a less slippery surface compared to filament silk, making it easier to cut, sew, and maintain during regular use.
Home and Interior Textiles
For interior applications, spun silk is used in cushion covers, curtains, and decorative fabrics where a natural texture is preferred. Its durability and reduced shine align well with contemporary interior design trends focused on understated materials.
Why Brands Are Shifting Toward Spun Silk Fabric
Brands adopting spun silk fabric are responding to both sustainability expectations and practical production needs. The fabric supports responsible sourcing narratives while offering consistent performance in large-scale manufacturing. Its compatibility with blended fibers also allows designers to fine-tune texture, strength, and cost without compromising environmental considerations.
As consumer awareness of textile sustainability increases, spun silk stands out as a material that balances ecological responsibility with functional value. This combination explains its growing presence in collections aimed at long-term wear and mindful consumption.


 中文简体
中文简体 Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch italiano
italiano
 previous post
previous post